遗传算法程序:
说明: fga.m 为遗传算法的主程序;采用二进制Gray编码,采用基于轮盘赌法的非线性排名选择, 均匀交叉,变异操作,而且还引入了倒位操作! function[BestPop,Trace]=fga(FUN,LB,UB,eranum,popsize,pCross,pMutation,pInversion,options)
%[BestPop,Trace]=fmaxga(FUN,LB,UB,eranum,popsize,pcross,pmutation)
% Finds a maximum of a function of several variables.
% fmaxga solves problems of the form:
%max F(X) subject to: LB <= X <=UB
%BestPop- 最优的群体即为最优的染色体群
%Trace- 最佳染色体所对应的目标函数值
%FUN- 目标函数
%LB- 自变量下限
%UB- 自变量上限
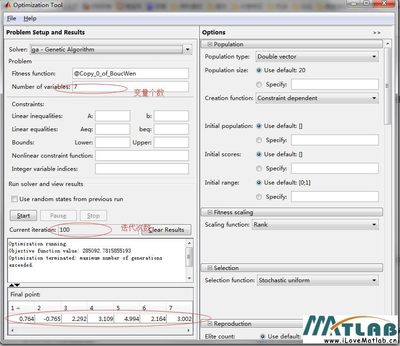
%eranum- 种群的代数,取100--1000(默认200)
%popsize- 每一代种群的规模;此可取50--200(默认100)
%pcross- 交叉概率,一般取0.5--0.85之间较好(默认0.8)
%pmutation- 初始变异概率,一般取0.05-0.2之间较好(默认0.1)
% pInversion- 倒位概率,一般取0.05-0.3之间较好(默认0.2)
%options- 1*2矩阵,options(1)=0二进制编码(默认0),option(1)~=0十进制编
%码,option(2)设定求解精度(默认1e-4)
%
%------------------------------------------------------------------------ T1=clock;
if nargin<3, error('FMAXGA requires at least threeinput arguments'); end
if nargin==3,eranum=200;popsize=100;pCross=0.8;pMutation=0.1;pInversion=0.15;options=[01e-4];end
if nargin==4,popsize=100;pCross=0.8;pMutation=0.1;pInversion=0.15;options=[01e-4];end
if nargin==5, pCross=0.8;pMutation=0.1;pInversion=0.15;options=[01e-4];end
if nargin==6, pMutation=0.1;pInversion=0.15;options=[01e-4];end
if nargin==7, pInversion=0.15;options=[0 1e-4];end
if find((LB-UB)>0)
error('数据输入错误,请重新输入(LB<UB):');
end
s=sprintf('程序运行需要约%.4f秒钟时间,请稍等......',(eranum*popsize/1000));
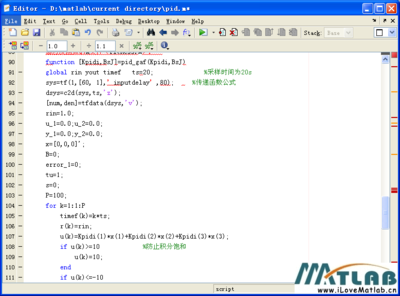
disp(s); global m n NewPop children1 children2 VarNum bounds=[LB;UB]';bits=[];VarNum=size(bounds,1);
precision=options(2);%由求解精度确定二进制编码长度
bits=ceil(log2((bounds(:,2)-bounds(:,1))' ./precision));%由设定精度划分区间
[Pop]=InitPopGray(popsize,bits);%初始化种群
[m,n]=size(Pop);
NewPop=zeros(m,n);
children1=zeros(1,n);
children2=zeros(1,n);
pm0=pMutation;
BestPop=zeros(eranum,n);%分配初始解空间BestPop,Trace
Trace=zeros(eranum,length(bits)+1);
i=1;
while i<=eranum
forj=1:m
value(j)=feval_r(FUN(1,:),(b2f(Pop(j,:),bounds,bits)));%计算适应度
end
[MaxValue,Index]=max(value);
BestPop(i,:)=Pop(Index,:);
Trace(i,1)=MaxValue;
Trace(i,(2:length(bits)+1))=b2f(BestPop(i,:),bounds,bits);
[selectpop]=NonlinearRankSelect(FUN,Pop,bounds,bits);%非线性排名选择
[CrossOverPop]=CrossOver(selectpop,pCross,round(unidrnd(eranum-i)/eranum));
%采用多点交叉和均匀交叉,且逐步增大均匀交叉的概率
%round(unidrnd(eranum-i)/eranum)
[MutationPop]=Mutation(CrossOverPop,pMutation,VarNum);%变异
[InversionPop]=Inversion(MutationPop,pInversion);%倒位
Pop=InversionPop;%更新
pMutation=pm0+(i^4)*(pCross/3-pm0)/(eranum^4);
%随着种群向前进化,逐步增大变异率至1/2交叉率
p(i)=pMutation;
i=i+1;
end
t=1:eranum;
plot(t,Trace(:,1)');
title('函数优化的遗传算法');xlabel('进化世代数(eranum)');ylabel('每一代最优适应度(maxfitness)');
[MaxFval,I]=max(Trace(:,1));
X=Trace(I,(2:length(bits)+1));
hold on; plot(I,MaxFval,'*');
text(I+5,MaxFval,['FMAX=' num2str(MaxFval)]);
str1=sprintf('进化到 %d 代 ,自变量为 %s 时,得本次求解的最优值%fn对应染色体是:%s',I,num2str(X),MaxFval,num2str(BestPop(I,:)));
disp(str1);
%figure(2);plot(t,p);%绘制变异值增大过程
T2=clock;
elapsed_time=T2-T1;
if elapsed_time(6)<0
elapsed_time(6)=elapsed_time(6)+60;elapsed_time(5)=elapsed_time(5)-1;
end
if elapsed_time(5)<0
elapsed_time(5)=elapsed_time(5)+60;elapsed_time(4)=elapsed_time(4)-1;
end %像这种程序当然不考虑运行上小时啦
str2=sprintf('程序运行耗时 %d 小时 %d 分钟 %.4f秒',elapsed_time(4),elapsed_time(5),elapsed_time(6));
disp(str2); %初始化种群
%采用二进制Gray编码,其目的是为了克服二进制编码的Hamming悬崖缺点
function [initpop]=InitPopGray(popsize,bits)
len=sum(bits);
initpop=zeros(popsize,len);%The whole zero encodingindividual
for i=2:popsize-1
pop=round(rand(1,len));
pop=mod(([0pop]+[pop 0]),2);
%i=1时,b(1)=a(1);i>1时,b(i)=mod(a(i-1)+a(i),2)
%其中原二进制串:a(1)a(2)...a(n),Gray串:b(1)b(2)...b(n)
initpop(i,:)=pop(1:end-1);
end
initpop(popsize,:)=ones(1,len);%The whole one encodingindividual %解码 function [fval] = b2f(bval,bounds,bits)
% fval - 表征各变量的十进制数
% bval - 表征各变量的二进制编码串
% bounds - 各变量的取值范围
% bits - 各变量的二进制编码长度
scale=(bounds(:,2)-bounds(:,1))'./(2.^bits-1); %The range of thevariables
numV=size(bounds,1);
cs=[0 cumsum(bits)];
for i=1:numV
a=bval((cs(i)+1):cs(i+1));
fval(i)=sum(2.^(size(a,2)-1:-1:0).*a)*scale(i)+bounds(i,1);
end %选择操作
%采用基于轮盘赌法的非线性排名选择
%各个体成员按适应值从大到小分配选择概率:
%P(i)=(q/1-(1-q)^n)*(1-q)^i, 其中P(0)>P(1)>...>P(n),sum(P(i))=1 function[selectpop]=NonlinearRankSelect(FUN,pop,bounds,bits)
global m n
selectpop=zeros(m,n);
fit=zeros(m,1);
for i=1:m
fit(i)=feval_r(FUN(1,:),(b2f(pop(i,:),bounds,bits)));%以函数值为适应值做排名依据
end
selectprob=fit/sum(fit);%计算各个体相对适应度(0,1)
q=max(selectprob);%选择最优的概率
x=zeros(m,2);
x(:,1)=[m:-1:1]';
[y x(:,2)]=sort(selectprob);
r=q/(1-(1-q)^m);%标准分布基值
newfit(x(:,2))=r*(1-q).^(x(:,1)-1);%生成选择概率
newfit=cumsum(newfit);%计算各选择概率之和
rNums=sort(rand(m,1));
fitIn=1;newIn=1;
while newIn<=m
ifrNums(newIn)<newfit(fitIn)
selectpop(newIn,:)=pop(fitIn,:);
newIn=newIn+1;
else
fitIn=fitIn+1;
end
end %交叉操作
function [NewPop]=CrossOver(OldPop,pCross,opts)
%OldPop为父代种群,pcross为交叉概率
global m n NewPop
r=rand(1,m);
y1=find(r<pCross);
y2=find(r>=pCross);
len=length(y1);
iflen>2&mod(len,2)==1%如果用来进行交叉的染色体的条数为奇数,将其调整为偶数
y2(length(y2)+1)=y1(len);
y1(len)=[];
end
if length(y1)>=2
for i=0:2:length(y1)-2
if opts==0
[NewPop(y1(i+1),:),NewPop(y1(i+2),:)]=EqualCrossOver(OldPop(y1(i+1),:),OldPop(y1(i+2),:));
else
[NewPop(y1(i+1),:),NewPop(y1(i+2),:)]=MultiPointCross(OldPop(y1(i+1),:),OldPop(y1(i+2),:));
end
end
end
NewPop(y2,:)=OldPop(y2,:); %采用均匀交叉
function [children1,children2]=EqualCrossOver(parent1,parent2) global n children1 children2
hidecode=round(rand(1,n));%随机生成掩码
crossposition=find(hidecode==1);
holdposition=find(hidecode==0);
children1(crossposition)=parent1(crossposition);%掩码为1,父1为子1提供基因
children1(holdposition)=parent2(holdposition);%掩码为0,父2为子1提供基因
children2(crossposition)=parent2(crossposition);%掩码为1,父2为子2提供基因
children2(holdposition)=parent1(holdposition);%掩码为0,父1为子2提供基因 %采用多点交叉,交叉点数由变量数决定 function[Children1,Children2]=MultiPointCross(Parent1,Parent2) global n Children1 Children2 VarNum
Children1=Parent1;
Children2=Parent2;
Points=sort(unidrnd(n,1,2*VarNum));
for i=1:VarNum
Children1(Points(2*i-1):Points(2*i))=Parent2(Points(2*i-1):Points(2*i));
Children2(Points(2*i-1):Points(2*i))=Parent1(Points(2*i-1):Points(2*i));
end %变异操作
function [NewPop]=Mutation(OldPop,pMutation,VarNum) global m n NewPop
r=rand(1,m);
position=find(r<=pMutation);
len=length(position);
if len>=1
for i=1:len
k=unidrnd(n,1,VarNum); %设置变异点数,一般设置1点
for j=1:length(k)
if OldPop(position(i),k(j))==1
OldPop(position(i),k(j))=0;
else
OldPop(position(i),k(j))=1;
end
end
end
end
NewPop=OldPop; %倒位操作 function [NewPop]=Inversion(OldPop,pInversion) global m n NewPop
NewPop=OldPop;
r=rand(1,m);
PopIn=find(r<=pInversion);
len=length(PopIn);
if len>=1
fori=1:len
d=sort(unidrnd(n,1,2));
if d(1)~=1&d(2)~=n
NewPop(PopIn(i),1:d(1)-1)=OldPop(PopIn(i),1:d(1)-1);
NewPop(PopIn(i),d(1):d(2))=OldPop(PopIn(i),d(2):-1:d(1));
NewPop(PopIn(i),d(2)+1:n)=OldPop(PopIn(i),d(2)+1:n);
end
end
end |
 爱华网
爱华网